A third of the way through!
After four months in 1918, I’ve become both more optimistic and more pessimistic about our present world. More optimistic because so many problems that seemed intractable back then, like the acceptability in mainstream circles of overt racism, sexism, and antisemitism, are gone now. More pessimistic because of all the new problems, like global warming, that people back then couldn’t have conceived of.
Okay, enough philosophizing. On to the best and worst of April 1918.
Best magazine: The Dial

The Dial is one of the most reliably interesting reads of 1918. It started out in 1840 as an outlet for the Transcendentalists (Louisa May Alcott’s father came up with the name) and was now a Chicago-based political and literary journal. H.L. Mencken wasn’t a fan—he ridiculed the “insane labeling and pigeon-holing that passes for criticism among the gifted Harvard boys of the Dial and the Nation”—but staff writer Randolph Bourne gave as good as he got, saying that Mencken and Theodore Dreiser “beat at a straw man of puritanism which, for the younger generation, has not even the vitality to be interesting.”*
The Dial did have a tendency to review seemingly every book that showed up on its doorstep, like Colorado, the Queen Jewel of the Rockies. But when a single (April 11) issue includes John Dewey on education, historian Charles Beard (who had recently resigned in protest from Columbia) on universities and democracy, Conrad Aiken on poetry,** and Bourne on immigrant fiction, I can forgive a lot.
Best short story: “The Swimming Pool” by Evelyn Campbell, Smart Set

I haven’t read many magazine short stories this month. In fact, I’ve read just one: this one. And I wouldn’t call it a great story. So this might strike you as a shoddy bit of best-and-worst selecting. But something about this story by Evelyn Campbell, a 22-year-old screenwriter and Ziegfeld Follies girl, got to me.
A woman, swimming in a pool as darkness falls, strikes up a conversation with a man. They’re both natural swimmers, creatures of the water, and during their brief conversation they fall a little in love.
Suddenly it was dusk. Not in the enclosure made brilliant by white bulbs, but up above in the oblong of dark blue sky where newly awakened stars began to show timid faces to their bolder rivals. They were in the deep water which lay densely beneath them. Again they turned upon their backs and floated.
As the woman leaves the country club with her horrible rich husband and their children, she passes the man, who’s wearing an ill-cut suit. Her daughter says, Oh, look, the new janitor. A typical Smart Set snappy ending. In most stories, though, the twist at the end is the point—the rest is just setup. Here, the spell that the water casts on the swimmers is the point, and the ending is just the resolution.
Some of Campbell’s descriptions work better than others—I can’t picture what “in the middle of the pool a big golden square turned the water to bright emerald” looks like—but she’s trying something other writers just weren’t doing in 1918. That is, Imagist poets were, but not magazine short story writers.
Best magazine cover: The Crisis

Even by 1918’s high standards, this was an exceptional month for magazine covers. I’ve posted pictures of several of them already (here and here and here). The standout, though, is the cover of the April issue of The Crisis, the NAACP magazine edited by W.E.B. Du Bois. It features a copy of a painting called “Lead Kindly Light,” made for the magazine by 34-year-old William Edouard Scott (and now owned by the Huntington Museum of Art in West Virginia).
Here’s how the magazine’s editorial, probably written by Du Bois, interprets the painting.
It is just an old lantern, filled with grimy oil. It cannot lead anywhere, yet its light leads. Its golden light streams through the night.
Whose is the light?
It is not the lantern’s. It simply seems to be the lantern’s radiance. It is the Light of the World and it leads not toward the millennium in the North, but out of the insult and prostitution and ignorance and lies and lynchings of the South—up toward a chance, a new chance,—nothing more. But thank God for that…
Lead, Kindly Light.
Worst magazine cover: Ladies’ Home Journal
This is a repeat, but nothing was going to beat this Ladies’ Home Journal cover, titled (by me) “Oh, how sweet! My boyfriend killed someone!”

Best poem: “Is It Worth While,” Violet Hunt, Poetry

Violet Hunt, ca. 1900
Reading Poetry magazine, you can see how living in 1918 was like living in two worlds. In the April 1918 issue, there’s page after page of purple mountains, and it could be 1868, and suddenly there’s Violet Hunt mourning her relationship with Ford Madox Hueffer (Ford), and it could be 1968.

You can read the rest of the poem here.
Faintest praise in a book review: T.S. Eliot, The Egoist

archive.org
This was a surprisingly competitive category. At first, this unsigned review in the April 11 Dial, of Lorinda Munson Bryant’s American Pictures and their Painters, looked like a shoo-in:
One sincerely wishes that Mrs. Bryant in her enthusiasm for nature, both inanimate and human, had focused her numerous descriptions of the subject matter of the paintings. That the painter has chosen to paint a wintry landscape…is surely no excuse for a genteel panegyric on winter, or that the artist has selected a human being…is no excuse for a general eulogy of mankind. In the family circle a little girl, it is true, may be a “darling,” but in a painting that may be the least interesting of her attributes….If the subject is a woman, and a thin one at that, the author thinks the artist would have been wiser to select a plumper and rosier model…Aside from these minor defects the book is a handy and valuable compendium.

From “Hearts of Controversy,” by Alice Meynell, second edition, 1918
But then I came across this review of Alice Meynell’s Hearts of Controversy by Apteryx, AKA T.S. Eliot, in the April issue of The Egoist, and we had a winner.
In its peculiar anti-style, Mrs. Meynell’s book, like all her books, is extremely well written, and she can incidentally pick out good bits from authors. If we can accept this attitude, we shall enjoy the book very much. And people who have a taste for that antiquated genre, that parlour-game, the Polite Essay—which consists in taking a tiny point and cutting figure eights around it, without ever uttering one’s meaning in plain words—will find in Mrs. Meynell’s last essay (“Charmain”) an almost perfect example of a forgotten craft which indeed had its attractions.
* * *
But we must learn to take literature seriously.
(Asterixes Apteryx’s.)
Best neologism: Surréaliste

Study for a portrait of Guillaume Apollinaire, Jean Metzinger, 1911
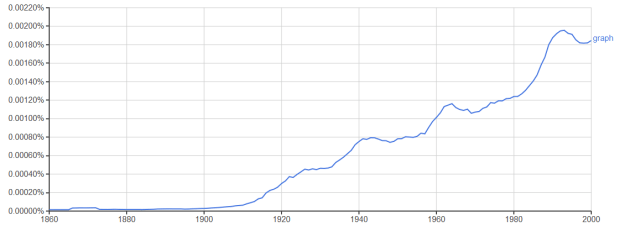
“SURRÉALISTE is the denomination M. Guillaume Apollinaire—there is no doubt his astounding name continues to have good reason for keeping well in evidence—has attached to his play, Les Mamelles de Tirésias,” the Paris correspondent for The Egoist tells us. I knew that the surrealist movement was just getting underway in 1918, but it seemed strange to think of the word itself being a novelty. So I crunched some big data—that is, did a Google Books N-Gram***—and it’s true, surreal and its variants were pretty much non-existent at that point. So what did people say when things were, you know, surreal? (UPDATE 1/16/2021: It turns out that “stream of consciousness” in a literary context was also coined this month, by May Sinclair in an article about novelist Dorothy Richardson in The Egoist, which I actually read without realizing “stream of consciousness” was making its debut.)

Best humor:

In The Bookman, there’s a report about the mystery surrounding the identity of the author of The Book of Artemas, a bestselling British spoof relating current events in biblical style. Was it G.K. Chesterton? J.M. Barrie? Hilaire Belloc? George Bernard Shaw? (It would turn out to be someone no one ever heard of named Arthur Telford Mason.) Here’s an excerpt:
5. Whilst Wudro, the son of Wyl, was tending his flock of young men in the pasture that is knowledge, and after he had taught them how they should go and what things they should know,
6. Behold, the men of Amer came unto him, saying, We have chosen thee for to rule over us; and we have brought thee an high hat for to wear as the badge of thine office; and the size of the hat, it is six and seven-eights.
7. And because he knew not what he was letting himself in for, he gave way to their importuning, and did put on the high hat, the size whereof was six and seven-eights.
8. And it came to pass that when the men of En fought against the men of Hu, they did send messengers unto the land of Amer for to buy them munitions for the war. And they took with them gold in great quantity wherewith to satisfy the merchants that did sell unto them. Therefor did the land of Amer prosper exceedingly.
Worst joke:

Judge, April 27, 1918
On to May!
*Kind of harsh, since Bourne was only six years younger than Mencken.
**He agrees with me about Christopher Morley’s goopiness.
***Which is really fun—you should try if you’re off Facebook and looking for new ways to waste time.